Engineering is the closest thing to magic that exists in the world.
~Elon Musk
To get the most out of Unistyles, it’s important to understand how it works and how it updates your styles.
A typical app consist of many StyleSheets. A StyleSheet is a JavaScript object that holds one or many styles. Each style is associated with native view.
What’s more important is that each StyleSheet is unique, tailored to the needs of the view it’s associated with, or to a shared component.
Your app’s StyleSheets
Unistyles needs to understand your StyleSheet dependencies in order to update them only when necessary. This process begins when Babel transforms your app’s code. At this stage, the Unistyles Babel plugin scans your StyleSheets and determines the dependencies for each style:
const styles = StyleSheet.create((theme, rt) => ({ // static: no dependencies container: { backgroundColor: 'red', }, // depends on theme and font scale text: { color: theme.colors.text, fontSize: rt.fontScale * 16 }, dynamic: (isOdd: boolean) => ({ // depends on theme color: isOdd ? theme.colors.primary : theme.colors.secondary, })})As you already know, Unistyles has no components. This means your native view hierarchy remains exactly the same as in your original code. The Babel plugin processes your components through our component factory to borrow refs and bind the ShadowNode with Unistyle.
You might be wondering, what is Unistyle? We refer to it as your StyleSheet style that have been parsed by the Unistyles compiler, and with the attached C++ state.

Your styles are transformed into Unistyles
We don’t just extract metadata from your styles. We do the same for your StyleSheet. On the C++ side, we know exactly which StyleSheet is static, which depends on a theme, and which Unistyles it contains. At this point, your app’s StyleSheets are reconstructed on the C++ side and stored in native C++ StyleSheets, which contain the parsed Unistyles.

C++ StyleSheets that contains parsed styles (Unistyles)
To make this process easier to visualize, imagine that the Unistyles engine is a production line. It takes your raw StyleSheets, parses them, and produces their C++ representation with Unistyles:
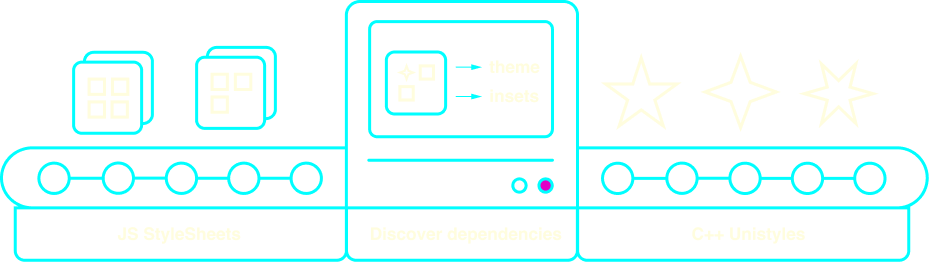
Unistyles workflow
When you access your StyleSheet styles in your component, you’ll get a regular JS object as expected. If your component re-renders, we simply return the same Unistyle that’s already parsed and stored in the cache.
To visualize the true power of Unistyles, imagine that some event occurs, such as:
At this point, the Unistyles algorithm scans the StyleSheetRegistry and looks for styles that depend on this event:
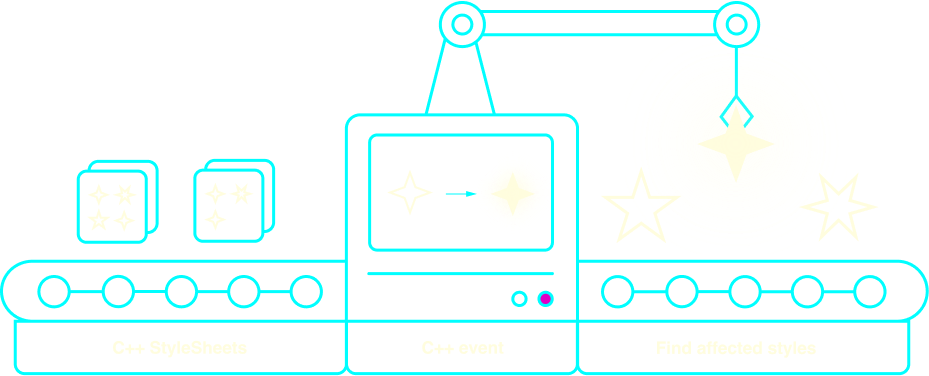
Finding affected styles
Affected styles are then re-computed to reflect the new state of your app.
With the list of affected styles, we can now browse the ShadowRegistry, where we keep the bindings between ShadowNode and Unistyles. In other words, we know which component relies on which style.
With all this information, we can translate the update into atomic ShadowTree instructions.
With Unistyles 2.0 or any other library, we would need to re-render your entire app to reflect the changes:
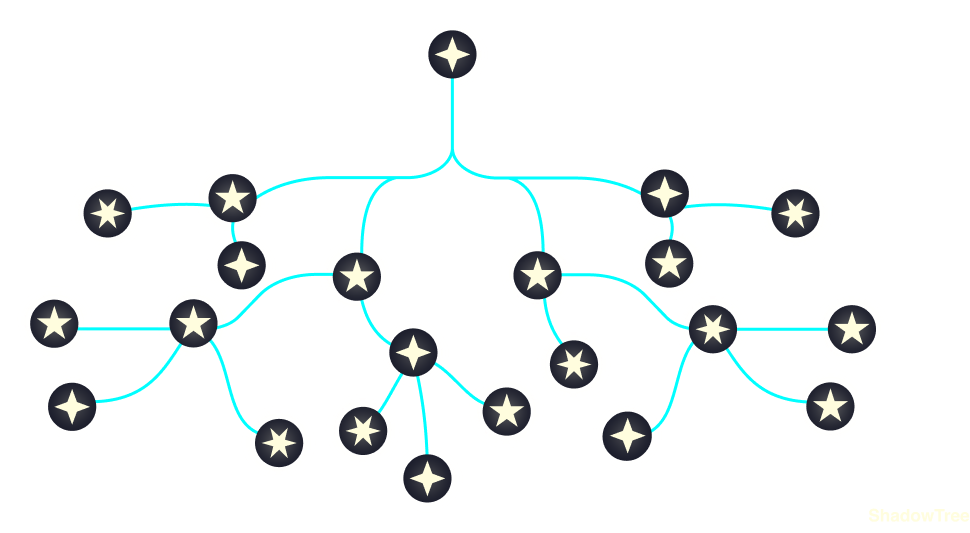
Regular flow: your app is re-rendered
Instead, with all the optimizations and features that Unistyles 3.0 brings, we can update your ShadowTree directly from C++:
Unistyles 3.0 updates only selected ShadowNodes from C++
With this architecture and the power of selective updates through ShadowTree, your components are never re-rendered.
Engineering is the closest thing to magic that exists in the world.
~Elon Musk